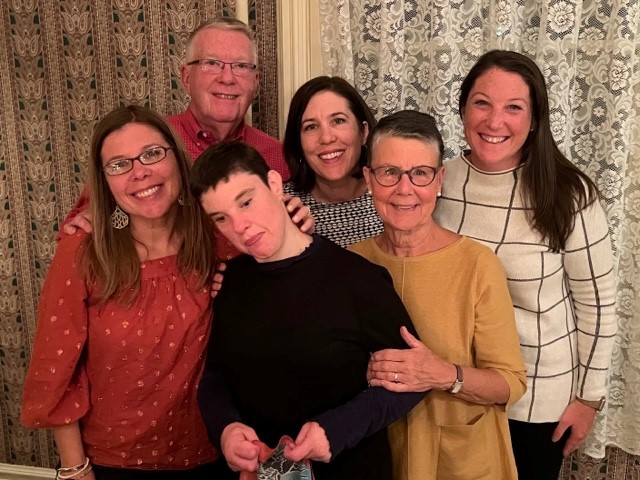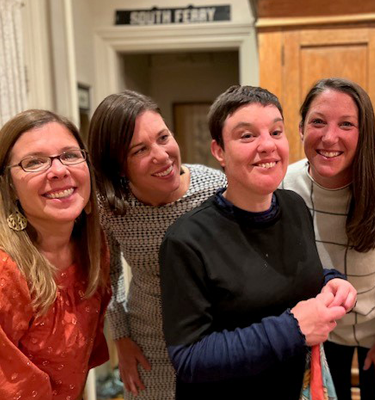Tips to Advocate During August Congressional Recess
 For some, August can be a time for camping trips, beach days, and other fun summer activities. But for members of Congress, August signals the start of Congressional Recess. During August recess, U.S. senators and representatives leave Washington, DC, and travel to their home states and districts to begin a fast-paced schedule of constituent meetings, town halls, and other community events.
For some, August can be a time for camping trips, beach days, and other fun summer activities. But for members of Congress, August signals the start of Congressional Recess. During August recess, U.S. senators and representatives leave Washington, DC, and travel to their home states and districts to begin a fast-paced schedule of constituent meetings, town halls, and other community events.
Last year, many of you answered the call to engage with your members of Congress by sharing your stories. We are so grateful to everyone who wrote, called, tweeted, and met with their representatives. Because of you, the concerns of the disability community were heard loudly in the halls of Congress.
With August nearing, it’s time to do what you do best and advocate for disability rights again!
August recess is your moment to provide members of Congress with a glimpse into your life and the issues that matter to you. With your stories echoing in their minds, these decision-makers can return to Washington ready to legislate meaningful change for the disability community.
To continue to build on the impact you have made in years past, we have prepared a few tips to keep in mind as you navigate this August Congressional Recess:
- Follow us on Facebook, X/Twitter, Instagram, and LinkedIn. Throughout August, we will be sharing actions you can take to advocate with your members of Congress.
- Visit our Action Center to find a few easy ways to take action. Tell your members of Congress to invest in home and community-based services and to update the Supplemental Security Income program for the first time in over 30 years.
- Visit your U.S. senators and representatives. You can look them up using our “Find your elected officials” tool. If you met with one of them during a previous August recess, make another appointment and strengthen your connection. And don’t forget to thank them for any past legislative actions that advanced disability rights!
- Follow your elected officials on social media. Learn what legislation your representatives are currently working on by finding their X/Twitter handles and following them.
- Connect with your local or state chapter of The Arc. Find your local chapter and reach out to them to learn about any meetings or other activities you can join.
- Attend town hall events. Many members of Congress host town hall meetings during the August recess to hear from their constituents. Contact your members of Congress or review their websites to see their town hall schedules.
We’re so proud of the way you have shown your commitment to disability rights over the years. Now, let’s build on that success! Connect with your representatives and share how their legislative actions (both past and present) affect your family. Your stories and perspective on important disability policy issues can prepare your legislators to fight for disability rights this year and beyond!





 His impact on students didn’t stop in the classroom. After his career as a teacher, he went on to become the Special Education Director in Philadelphia and now teaches graduate school, supervises teachers, and was just appointed by the Governor to serve on Pennsylvania’s Special Education Advisory Panel. He also continued to volunteer with The Arc. “I think I did everything possible with The Arc.” In 2005, The Arc of Pennsylvania asked Ken to represent The Arc on the state’s Right to Education Task Force, which later led to his joining the Boards of The Arc of Philadelphia and The Arc of Pennsylvania, where he served as president of both organizations. He learned more and more about The Arc of the United States and was eager to get involved. He went to National Conventions, joined Committees, and eventually joined the national Board. “I went from organizing days at the zoo to becoming the national President—I was flabbergasted,” shares Ken.
His impact on students didn’t stop in the classroom. After his career as a teacher, he went on to become the Special Education Director in Philadelphia and now teaches graduate school, supervises teachers, and was just appointed by the Governor to serve on Pennsylvania’s Special Education Advisory Panel. He also continued to volunteer with The Arc. “I think I did everything possible with The Arc.” In 2005, The Arc of Pennsylvania asked Ken to represent The Arc on the state’s Right to Education Task Force, which later led to his joining the Boards of The Arc of Philadelphia and The Arc of Pennsylvania, where he served as president of both organizations. He learned more and more about The Arc of the United States and was eager to get involved. He went to National Conventions, joined Committees, and eventually joined the national Board. “I went from organizing days at the zoo to becoming the national President—I was flabbergasted,” shares Ken.






 Debbi’s son Josh was born eight weeks early with a grade four brain hemorrhage. As she shares, “He was one of the sickest babies in the neonatal intensive care unit. It started our roller coaster of a journey of having a child with complex medical needs and disabilities.”
Debbi’s son Josh was born eight weeks early with a grade four brain hemorrhage. As she shares, “He was one of the sickest babies in the neonatal intensive care unit. It started our roller coaster of a journey of having a child with complex medical needs and disabilities.” Out of crisis came purpose. Debbi soon immersed her family in The Arc’s chapter support systems, connecting her sons to sibling workshops and herself to a parent networking group. “We still count on those relationships for support today,” added Debbi.
Out of crisis came purpose. Debbi soon immersed her family in The Arc’s chapter support systems, connecting her sons to sibling workshops and herself to a parent networking group. “We still count on those relationships for support today,” added Debbi.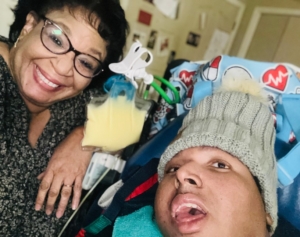 Once The Arc of the United States got word of Debbi’s powerhouse advocacy, we invited her to apply for the Board. Her proudest volunteer moments have been spearheading the creation of The Arc’s
Once The Arc of the United States got word of Debbi’s powerhouse advocacy, we invited her to apply for the Board. Her proudest volunteer moments have been spearheading the creation of The Arc’s 
 Working with people with disabilities is Lawrence’s long-time passion. He has worked as a direct support professional (DSP) in New York and Texas, both before and after serving in the Army. As a DSP, Lawrence takes pride in the trusted role he has in the lives of people with disabilities. He helps transport people to and from appointments, gives medicine, cooks, cleans, dresses, changes, and feeds people who may not be able to do these things for themselves. He even seeks out specialized training that is needed to support people who have challenging behaviors that may result in injury to themselves and others.
Working with people with disabilities is Lawrence’s long-time passion. He has worked as a direct support professional (DSP) in New York and Texas, both before and after serving in the Army. As a DSP, Lawrence takes pride in the trusted role he has in the lives of people with disabilities. He helps transport people to and from appointments, gives medicine, cooks, cleans, dresses, changes, and feeds people who may not be able to do these things for themselves. He even seeks out specialized training that is needed to support people who have challenging behaviors that may result in injury to themselves and others.
 Julia started attending a pre-school run by United Cerebral Palsy, where they received a flyer for a family event hosted by AHRC New York City. The whole family spent a Saturday afternoon connecting with other parents, siblings, and children with disabilities.
Julia started attending a pre-school run by United Cerebral Palsy, where they received a flyer for a family event hosted by AHRC New York City. The whole family spent a Saturday afternoon connecting with other parents, siblings, and children with disabilities.